- Home
-
Test Categories
- Diabetes
- Urinary
- Thyroid
- RTPCR
- Genetic
- Cancer
- Haematology
- Biochemistry
- Serology & Immunology
- Clinical Pathology
- Cytology
- Microbiology
- Endocrinology
- Histopathology
- MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
- Pregnancy(Biochemistry)
- Liver
- Prostate
- Fertility
- Gastro
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Heart
- Kidney
- Vitamins
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Anemia
- Fever
- Allergy
- Blood Tests Rare
- Profiles
- Packages
- About Us
- Why Choose Us
- Upload Prescription
- Corporate Wellness
- Contact Us
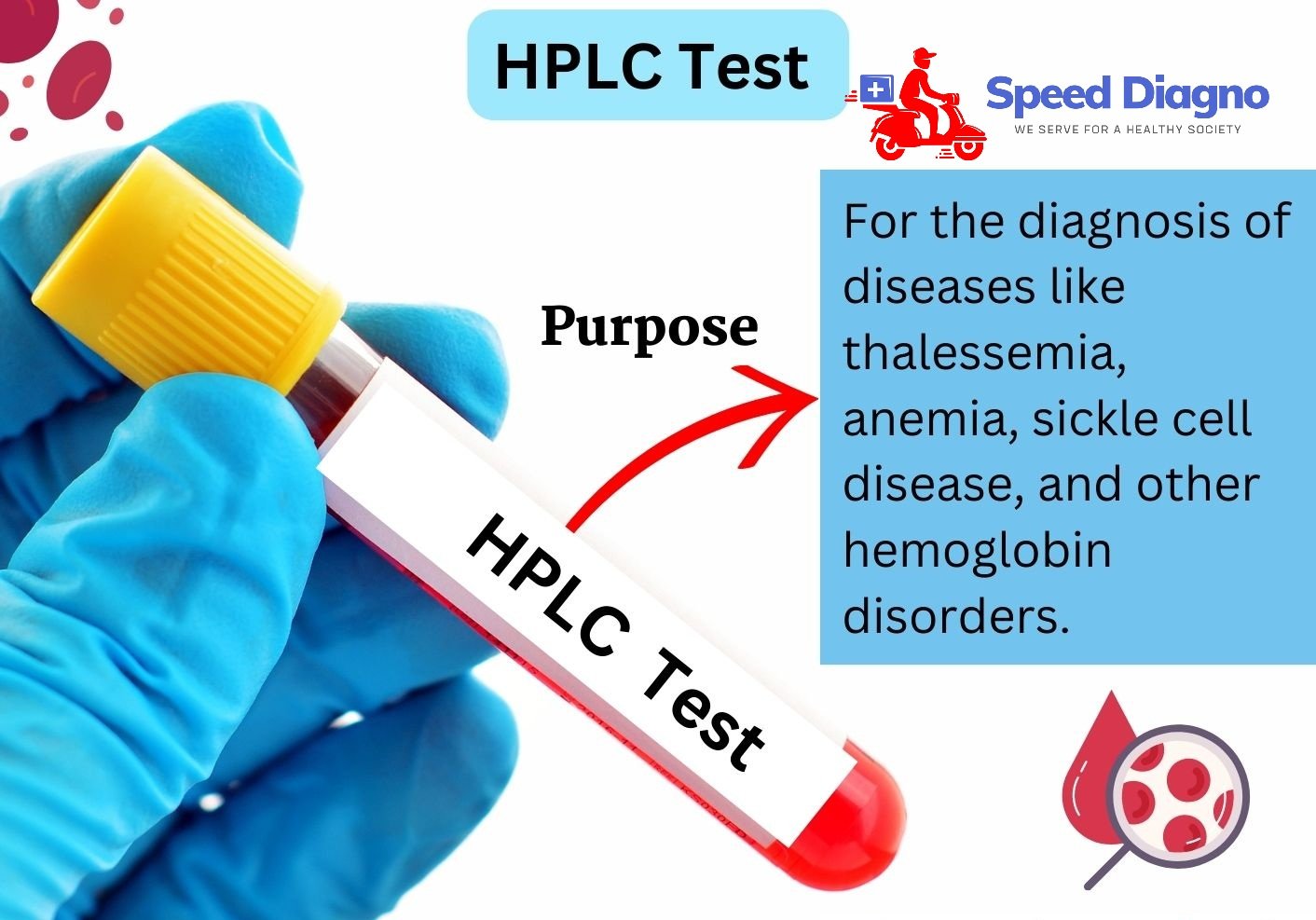
-
Overview
Hemoglobinopathy testing by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a method used to identify and analyze various hemoglobin disorders. This technique is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions like sickle cell disease, thalassemia, and other hemoglobin variants.
Understanding the Process:
Sample Collection: A blood sample is collected, usually from a vein in the arm.
Preparation: The hemoglobin in the blood sample is extracted and prepared for analysis.
Chromatography: The prepared sample is injected into an HPLC system. In HPLC, the sample is separated as it passes through a column packed with a stationary phase. Different types of hemoglobin proteins interact differently with the stationary phase, allowing for their separation.
Detection and Analysis: As the hemoglobin proteins emerge from the column, they are detected and quantified. The HPLC system generates a chromatogram—a graph that displays the different types of hemoglobin and their relative concentrations.
Identification: The pattern of peaks in the chromatogram corresponds to various types of hemoglobin. By comparing these patterns to known standards, specific hemoglobin variants or abnormalities can be identified.
Uses of Hemoglobinopathy Testing by HPLC:
- Diagnosing Hemoglobin Disorders: Identifies conditions like sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, and other hemoglobin variants.
- Newborn Screening: Often used in newborn screening programs to detect hemoglobinopathies early in life.
- Genetic Counseling: Helps in assessing risk and providing information for family planning and management of hemoglobin disorders.
- Monitoring and Management: Used to monitor the progression or management of known hemoglobinopathies.
Interpreting Results:
- Normal Hemoglobin Patterns: Show typical peaks corresponding to normal hemoglobin types like Hemoglobin A (HbA), Hemoglobin A2 (HbA2), and Hemoglobin F (HbF).
- Abnormal Patterns: May show peaks corresponding to abnormal hemoglobin types, such as Hemoglobin S (HbS) in sickle cell disease or Hemoglobin C (HbC) in HbC disease.
Advantages of HPLC for Hemoglobinopathy Testing:
- High Precision: Provides accurate separation and quantification of different hemoglobin types.
- Reproducibility: Offers consistent results in repeated tests.
- Sensitivity: Capable of detecting low levels of abnormal hemoglobin variants.
Overall, HPLC is a powerful and reliable method for diagnosing and managing hemoglobin disorders, providing valuable information for both medical professionals and patients.
All test groups and subgroup
-
HAEMOGLOBIN ELECTROPHORESIS
-
Z11 (denatured Hb A)
-
Unknown Unidentified Peak
-
HbA
-
HbA2
-
Hb C
-
Hb D
-
HbF
-
Hb S
-
COMMENTS
-
